turtlebot2-tutorials
Network Setup
Connect to a Wireless, Ethernet, or Cellular network using the Network Manager (upper right corner of desktop).
![]()
Using the hostname command in Linux, we are able to dynamically load the IP of the computer that will be on the Turtlebot so that less configuration is needed.
- You can find the IP of a computer by opening a terminal and typing:
hostname -I - Add the network parameters to your BashRC for the turtlebot computer
(bashrc is a file that configures the Linux shell environment)- Open a new terminal on the turtlebot computer and type the following:
(Breakdown of commands explained in the next section of this document)echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://\$\(hostname -I\):11311 >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_IP=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_HOME=\~/.ros >> ~/.bashrc(The backwards slash
\is an escape character in a Linux terminal shell)
- Open a new terminal on the turtlebot computer and type the following:
- Add the network parameters to your BashRC for the master computer:
- Open a new terminal on the master computer, and type the following:
(ReplaceIP_OF_TURTLEBOTwith the ip found in step1)echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://IP_OF_TURTLEBOT:11311 >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_IP=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc echo export ROS_HOME=\~/.ros >> ~/.bashrc
- Open a new terminal on the master computer, and type the following:
- Verify that the commands have been properly and printed to the bashrc file:
- Open a new terminal on both the master computer and the turtlebot computer
gedit ~/.bashrc- Scroll all the way down, and verify that the end of the file looks like this:
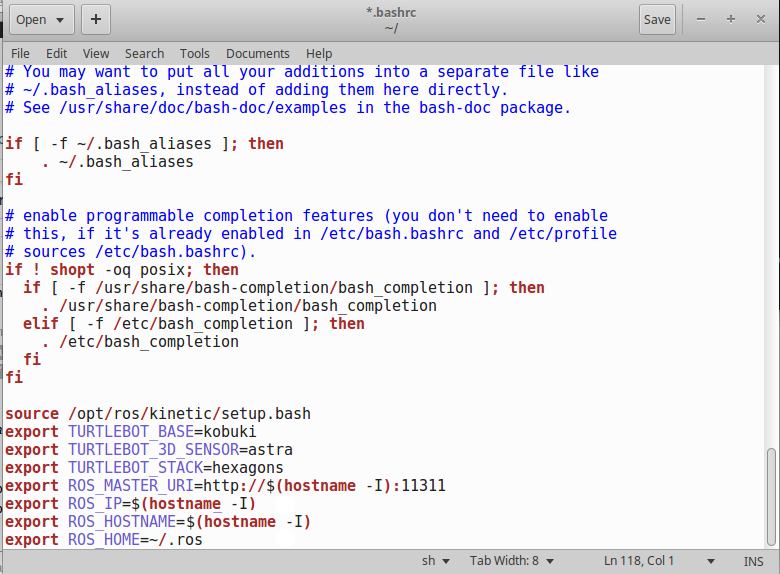
- Open a new terminal on both the master computer and the turtlebot computer
- Load the new environment variables above into your active terminal window
- On both Master and Turtlebot computers, open a terminal and type:
source ~/.bashrc
- On both Master and Turtlebot computers, open a terminal and type:
Command Breakdown
echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://\$\(hostname -I\):11311 >> ~/.bashrc
echo is a Linux command that prints text to a designated output (default is the terminal)
export is a Linux shell command that handles variables in the shell environment
ROS_MASTER_URI is the network address for a ROS instance to contact a ROS Master Server
http://\$\(hostname -I\):11311 sets the designated network address using the current IP found by the hostname command, and the \ are escape characters to prevent the hostname command from being run in the terminal
>> ~/.bashrc tells the echo command to send the output to the file ~/.bashrc
echo export ROS_IP=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc
echo is a Linux command that prints text to a designated output (default is the terminal)
export is a Linux shell command that handles variables in the shell environment
ROS_IP is the network address for a ROS instance to contact a ROS Master Server
\$\(hostname -I\) sets the designated network address using the current IP found by the hostname command, and the \ are escape characters to prevent the hostname command from being run in the terminal
>> ~/.bashrc tells the echo command to send the output to the file ~/.bashrc
echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=\$\(hostname -I\) >> ~/.bashrc
echo is a Linux command that prints text to a designated output (default is the terminal)
export is a Linux shell command that handles variables in the shell environment
ROS_HOSTNAME is the name of the computer on a network, used for communication on a local network
\$\(hostname -I\) sets the designated network name using the current hostname found by the hostname command, and the \ are escape characters to prevent the hostname command from being run in the terminal
>> ~/.bashrc tells the echo command to send the output to the file ~/.bashrc
echo export ROS_HOME=\~/.ros >> ~/.bashrc
echo is a Linux command that prints text to a designated output (default is the terminal)
export is a Linux shell command that handles variables in the shell environment
ROS_HOME is the environment variable for the location of the ROS home folder
\~/.ros is the directory in Linux for the location of the ROS home folder
Network Testing
ROS requires completely free network connectivity between the Turtlebot and the Master computer.
- Test the Ping command between the Master and the Turtlebot:
- On the master computer, open a new terminal:
ping IP_OF_TURTLEBOT- You should see the following returned if the Turtlebot is on the network:
PING IP_OF_TURTLEBOT (IP_OF_TURTLEBOT) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from IP_OF_TURTLEBOT: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=66.8 ms
- On the master computer, open a new terminal:
- Try connecting to the ROS Master server hosted on the Turtlebot
- On the Turtlebot, open a new terminal and type:
roscore
- On the master computer, open a new terminal and type:
rostopic list
- If successful, you should see the following output:
/rosout /rosout_agg
- On the Turtlebot, open a new terminal and type:
Troubleshooting
If your laptop cannot connect to the network, ensure that you installed the proprietary drivers.
If you continue to have issues, check out the ROS Network Setup Page